前言
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.12277.pdf
代码:https://github.com/universal-ie/UIE
动机
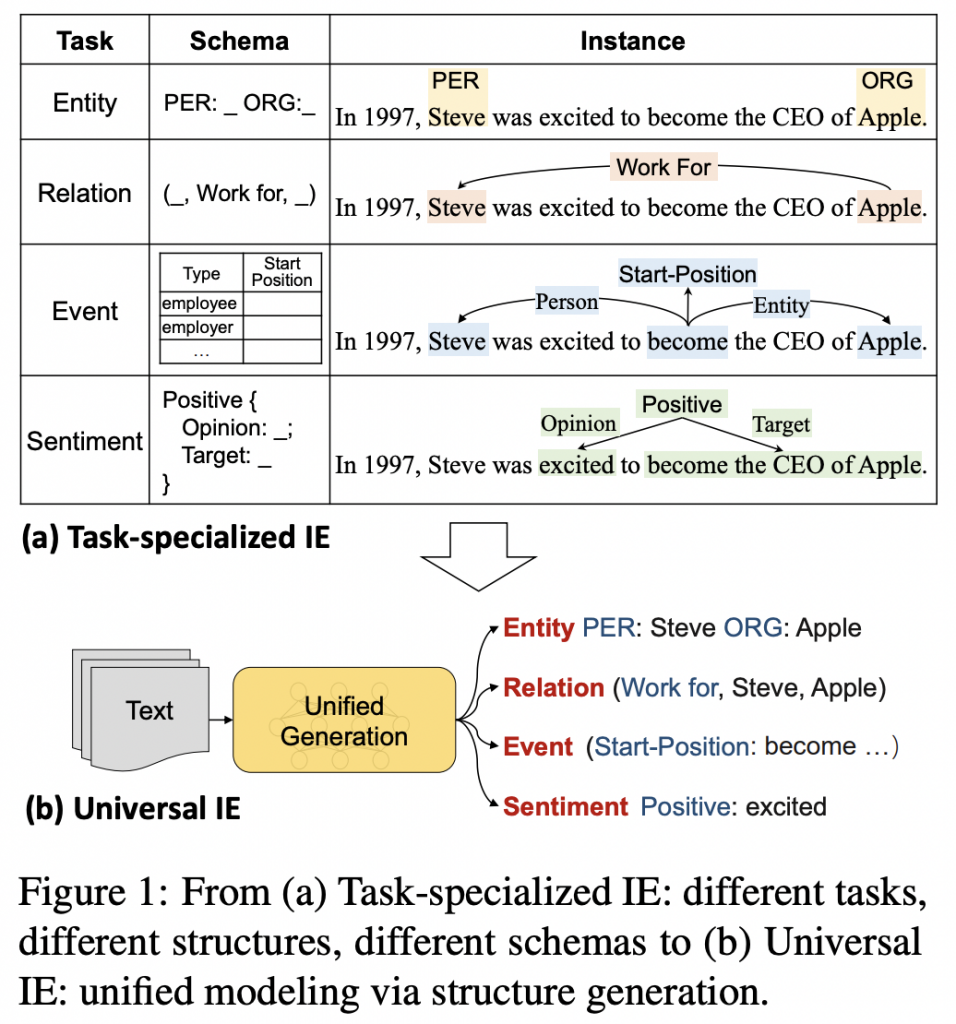
- 信息抽取旨在从非结构化文本中识别并结构化用户指定的信息(user-specified information)
- IE任务是高度多样化的,由于:
- varying targets(entity / relation / event / sentiment…)
- heterogeneous structures(span / triplet / record…)
- demand-specific schemas
- 然而,目前,多数方法是任务特定的(task-specialized),导致对于不同的IE任务需要构建:
- dedicated architectures(专门的结构)
- isolated models(孤立的模型)
- specialized knowledge sources(利用专门的知识源)
- 上述,任务特定的解决方案,阻碍了IE系统的:
- rapid architecture development(快速的结构发展):为大量的IE tasks / settings / scenarios 构建专门的结构过于复杂
- effective knowledge sharing(有效的知识共享):孤立的模型限制了相关任务或者设置之间的知识共享
- quick cross-domain adaptation(快速的跨领域适应):为不同的任务构建数据集:成本高、耗时
- 由此,论文提出Universal IE,即:
- 统一建模不同的IE任务
- 自适应地预测异构的结构
- 有效从不同数据源进行学习
- 挑战:如何自适应地控制抽取过程?
- 不同的目标结构
- 不同的schema
主要贡献
- 提出了a unified text-to-structure generation architecture
- 设计structured extraction language和structural schema instructor(SSI)
- 首个text-to-generation的预训练抽取模型,对后续研究有益
- 在低资源、少样本场景中表现出on-demand adaptation ability,验证了方法的有效性、通用性、可迁移性
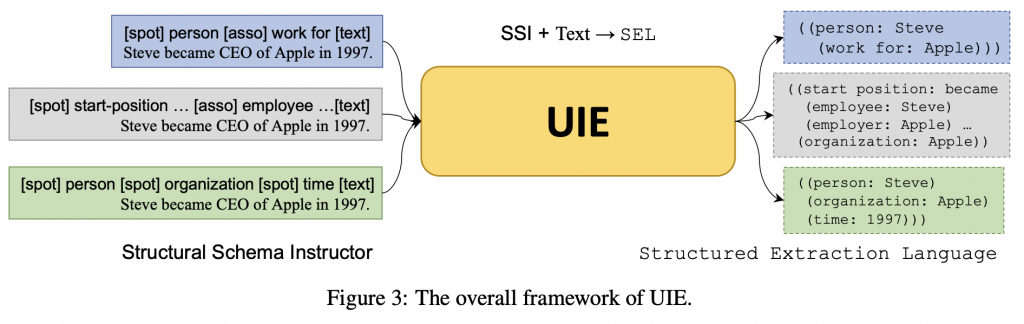
方法创新(SSI+Text⇒SEL)
UIE结构图
UIE方法
- 将所有的IE任务都建模为 text-to-structure transformations
- 将不同的任务都分解为一系列的原子转化操作,包括:
- spotting:
- 定位与给定的语义类型相关的span
- 例如:steve是一个person实体
- associating:
- 链接不同的span,并给他们分配预定义的schema涉及的语义角色
- 例如:将steve和apple链接,分别将其视为work-for关系的arg1和arg2
- spotting:
- 上述做法可以使所有的IE任务都共享相同的、底层的spotting和associating操作
- 将不同的任务都分解为一系列的原子转化操作,包括:
- structured extraction language(SEL)(为了建模不同的IE结构)
- 基本元素:
- SpotName:span的类型
- AssoName:association的类型
- InfoSpan:具体的span内容
- 结构:( Spot Name:Info Span (Asso Name:Info Span) )
- 基本元素:

- structural schema instructor(SSI)(为了自适应地生成不同的目标结构)
- a schema-based prompt mechanism,用来控制:
- what to spot
- what to associate
- what to generate
- 构建提示作为输入,基本元素:
- SpotName
- AssoName
- special symbols([spot] / [asso] / [text])
- 结构:[spot] xx [spot] xx … [asso] xx [asso] xx … [text] x_1, x_2, … , x_n
- a schema-based prompt mechanism,用来控制:
- A large-scale pre-trained text-to-structure model(为了从不同数据源学习通用的IE能力)
- 三个预训练数据集
- D_pair
- D_text
- D_record
- 三个任务,联合训练
- D_pair:同时优化编码器、解码器
- D_text:同时优化编码器、解码器(masked生成)
- D_record:仅优化解码器(语言模型)
- 微调:防止暴露偏差,引入rejection mechanism (RM),即引入噪音,例如(facility: [NULL])
- 三个预训练数据集
- 整体的流程:
- 根据任务 / schema,构建SSI
- 拼接SSI和text,输入模型
- 生成SEL
- 后处理形成最终结果